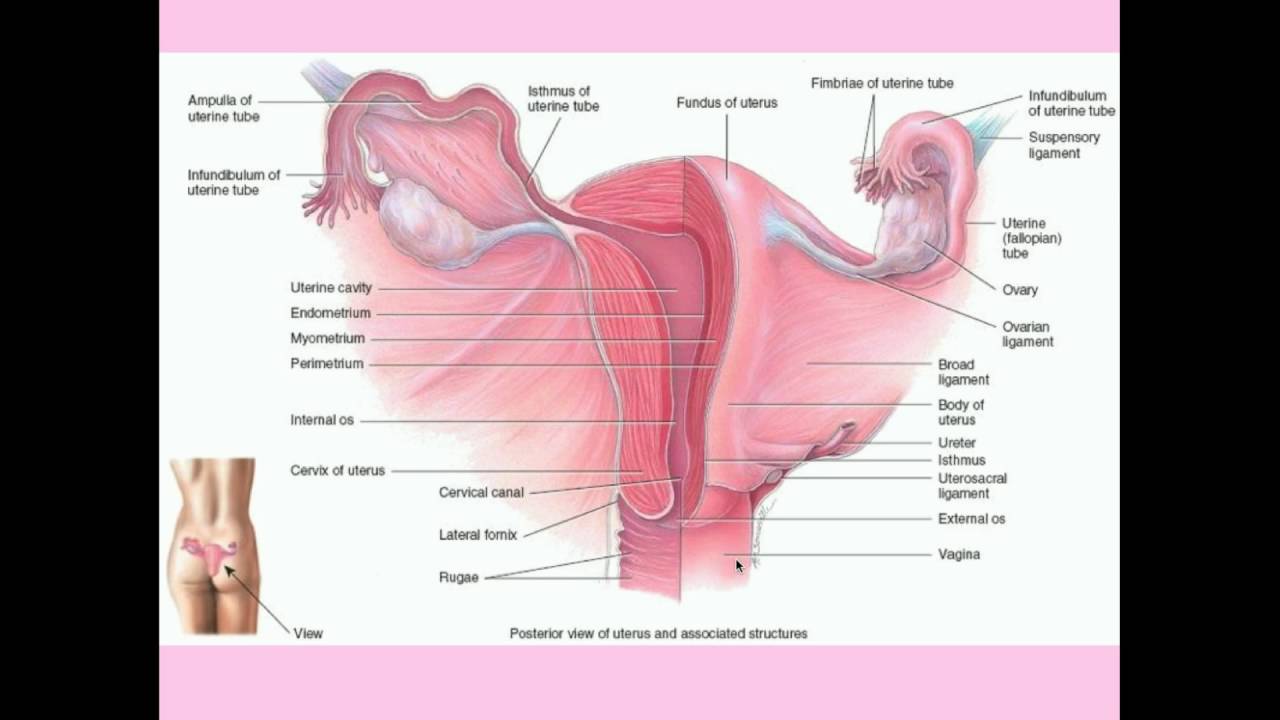
Cervix cancer, also known as cervical cancer, develops in the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It is one of the most preventable cancers due to its strong link with persistent HPV infections. This page provides a comprehensive overview of cervix cancer, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention methods, with expert insights from Dr. Saurabh Phadnis in London.
Cervix cancer, also known as cervical cancer, is a malignant tumour that arises from the cervix, the opening between the uterus and the vagina. Colposcopy is commonly used to closely examine the cervix for abnormal changes when cervical cancer is suspected.
Most cases of cervix cancer are linked to a long-term infection with high-risk strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). These infections cause cellular changes in the cervix, which can eventually lead to cancer.
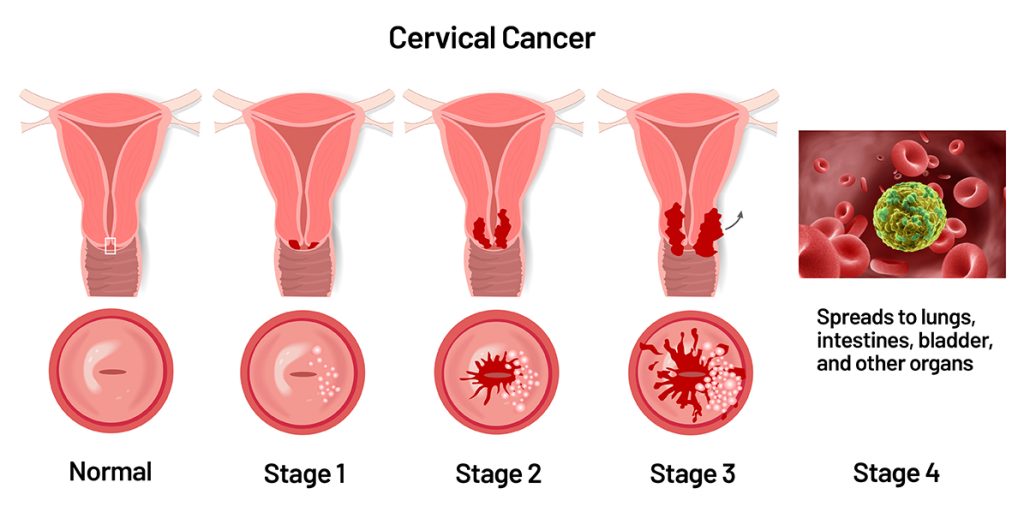
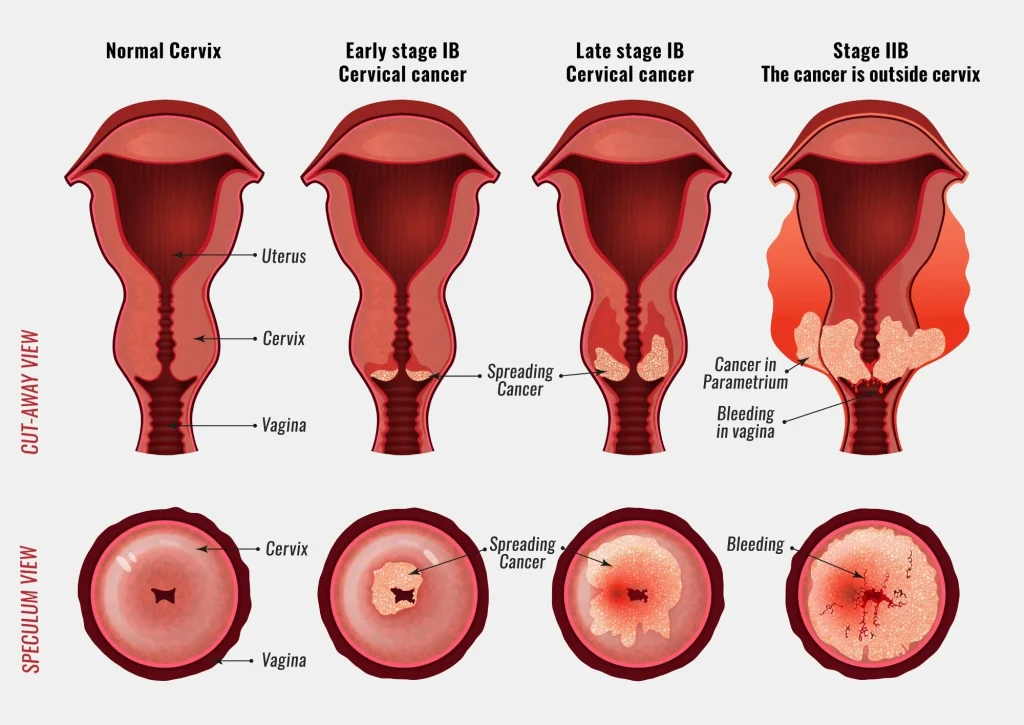
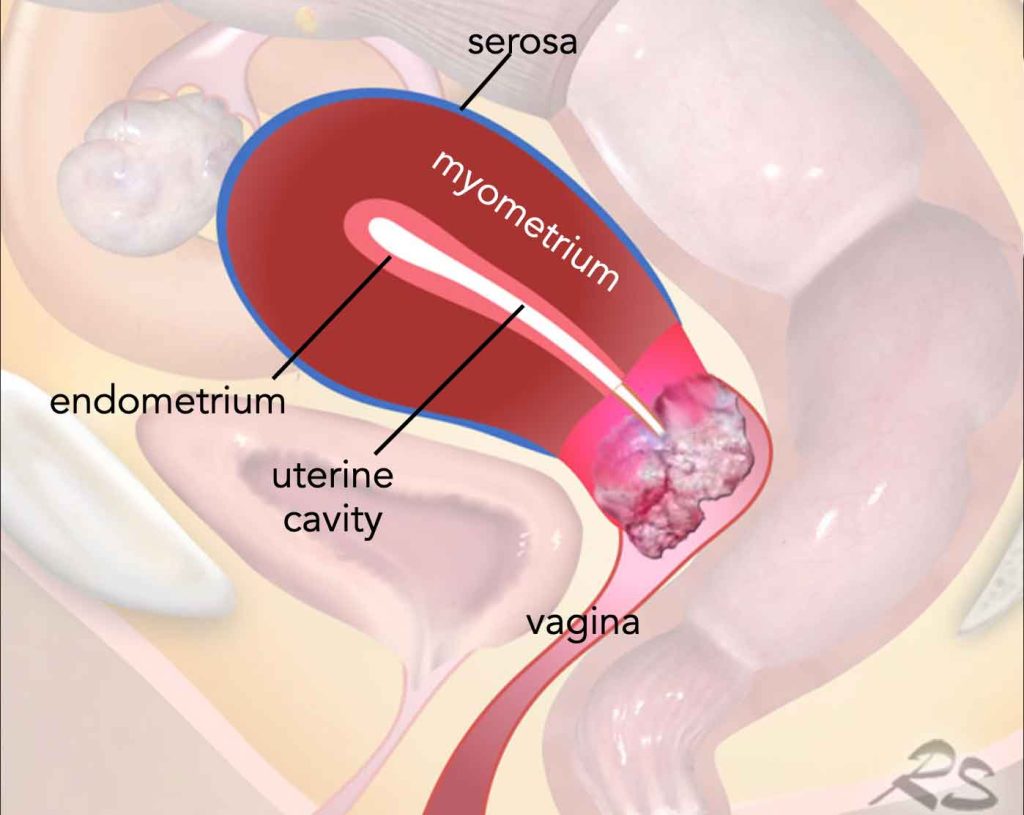
There are two main types of cervix cancer:
Pap Smear (Pap Test): The most common screening method. It involves collecting cells from the cervix to look for abnormal or precancerous changes.
HPV Test: This test detects high-risk strains of HPV that may cause cervical cancer. It is often done alongside a Pap test.
Colposcopy: If a Pap smear shows abnormalities, a colposcopy may be performed, where a special magnifying instrument is used to examine the cervix closely.
This diagnostic procedure plays an important role in guiding Cervical Cancer Treatment by helping specialists assess abnormal cervical cells accurately.
Biopsy: If abnormal tissue is detected, a biopsy is performed to remove a small sample of tissue from the cervix for examination.
Imaging Tests: In cases where cancer is suspected to have spread, imaging tests like MRI or CT scan CT scans, MRIs, or ultrasounds are used to assess the extent of cancer.
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill or shrink cancer cells. It is often combined with radiation therapy in advanced stages of the disease.
Cervix cancer is a serious health concern, but with early detection and appropriate treatment, the chances of successful outcomes are significantly improved. Regular screenings, the HPV vaccine, and a healthy lifestyle are key preventive measures.
If you’re in London, consult with Dr. Saurabh Phadnis for expert guidance on diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of cervical cancer, including Gynaecological Cancer care. Stay informed, and take proactive steps to ensure your health and well-being.
If you’re concerned about Cervix cancer, private consultations are available with Dr. Saurabh Phadnis, leading Gynaecologist, Oncologist, Surgeon, and Co-Lead Colposcopist based in London; specialising in gynaecological cancer. You can visit his clinic or call directly to book an appointment and receive expert care, advice, and personalised treatment.
Early stages of cervix cancer often have no symptoms, which is why regular screenings are so important. As the cancer progresses, symptoms such as abnormal bleeding, unusual vaginal discharge, and pelvic pain may appear.
The best preventive measures include getting vaccinated against HPV, having regular Pap smears, using safe sexual practices, and quitting smoking.
Treatment options for cervix cancer include surgery (such as a hysterectomy or cone biopsy), or combination of radiation therapy and, chemotherapy, and newer therapies like immunotherapy.
Yes, cervix cancer can be detected early with regular screenings like the Pap test and HPV test, allowing for timely intervention and higher survival rates.
The survival rate for cervix cancer is high when diagnosed early. The five-year survival rate for localized cervical cancer is over 90%, highlighting the importance of early detection.
Specialising in the field of gynaecological cancer, covering the entire spectrum from diagnosis to treatment and post-treatment care.