Gynaecological cancer is a term used for cancers that arise from the female reproductive organs, including the ovaries, cervix, uterus, vulva, and vagina. It is a group of cancers that can affect women at any age, though they are most commonly diagnosed in women over 50. Dr. Saurabh Phadnis, based in London, emphasizes the importance of early detection, as it significantly increases the chances of successful treatment.
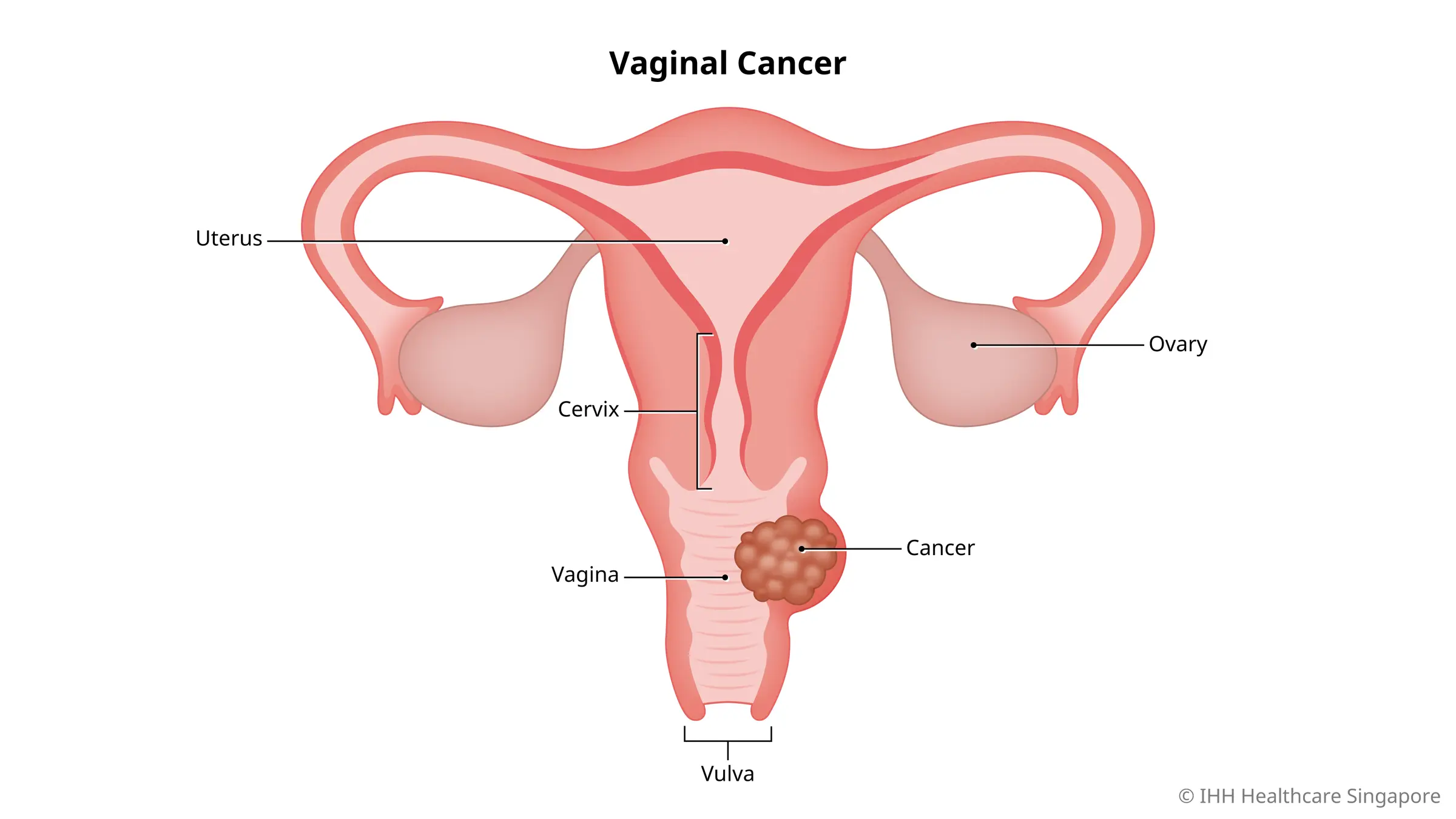
Gynaecological cancer refers to any cancer that arises from the female reproductive organs, including the ovaries, uterus, cervix, such as Cervix Cancer, vulva, and vagina.
It’s a term used to describe a group of cancers that can affect women at various stages of life, with early detection being critical to successful treatment and survival.

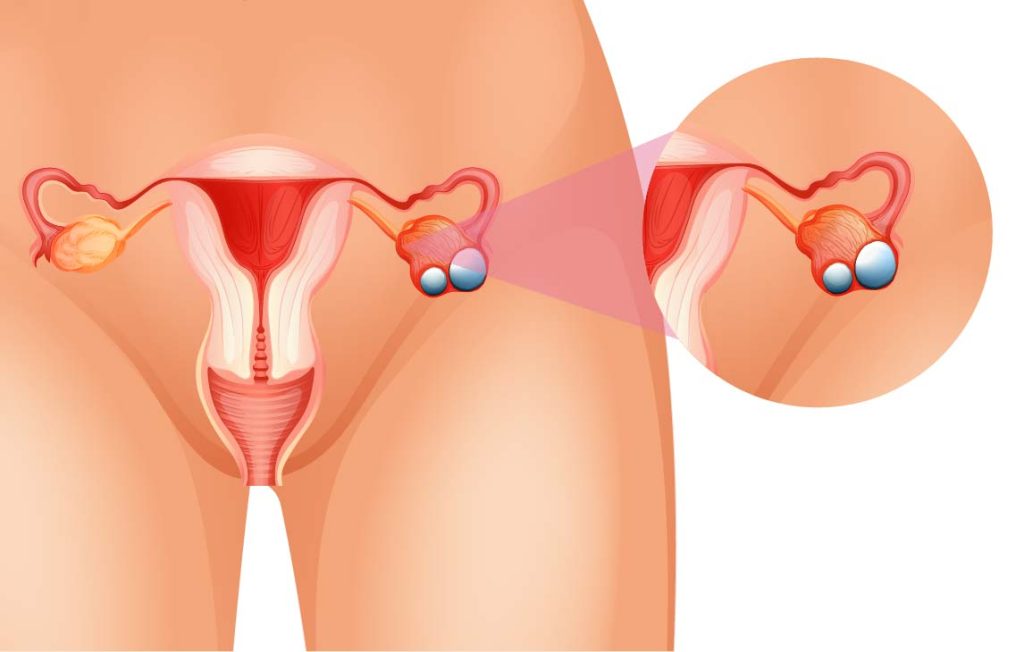
Specific Symptoms by Cancer Type
Cervical Cancer:
Uterine (Endometrial) Cancer:
Vulvar Cancer:
A pelvic exam allows the doctor to feel the ovaries for any abnormal growths or tenderness.
A pelvic ultrasound helps detect any cysts, tumours, or irregularities in the ovaries.
A Pap smear is a routine test for cervical cancer. It can detect abnormal cells in the cervix that may develop into cancer over time. HPV testing can also identify the presence of high-risk HPV strains that are linked to cervical cancer.
A biopsy involves taking a tissue sample from the ovaries to check for cancer cells under a microscope. This is typically done if a tumour is detected.
: A blood test measuring the level of CA-125, a protein often elevated in Ovary Cancer patients.

Surgery is often the first-line treatment for many types of gynaecological cancer. It involves removing the tumor or, in some cases, affected organs such as the uterus, ovaries, or cervix.
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
Radiation therapy involves high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells.
Targeted therapy specifically targets cancer cells, limiting damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
For advanced-stage cancer, palliative care focuses on managing symptoms and improving the patient’s quality of life.
The HPV vaccine protects against the strains of the virus that cause the majority of cervical cancers.
Maintaining a healthy weight, regular physical activity, and a balanced diet can reduce the risk of developing endometrial and ovarian cancers.
Regular Pap smears and HPV tests for cervical cancer can help detect abnormalities early, before they develop into cancer, and may also support early detection of related conditions, such as Fallopian Tube Cancer.
For women with a family history of gynaecological cancer, genetic testing (e.g., BRCA testing) can help assess the risk and guide preventative measures.
If you’re concerned about Gynaecological Cancer, private consultations are available with Dr. Saurabh Phadnis, leading Gynaecologist, Oncologist, Surgeon, and Co-Lead Colposcopist based in London; specialising in gynaecological cancer. You can visit his clinic or call directly to book an appointment and receive expert care, advice, and personalised treatment.
Gynaecological cancer refers to cancers that arise from affect the female reproductive organs, such as the ovaries, uterus, cervix, vulva, and vagina. Early detection is key to successful treatment.
Common symptoms include abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, bloating, and pain during intercourse. Specific symptoms depend on the type of cancer.
Diagnosis involves a pelvic exam, imaging tests (like ultrasound and MRI), biopsies, Pap smears, and blood tests.
While not all gynaecological cancers can be prevented, vaccines (e.g., for HPV), regular screenings, and a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk.
Treatment may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapies. The choice depends on the cancer type and stage.
Specialising in the field of gynaecological cancer, covering the entire spectrum from diagnosis to treatment and post-treatment care.